In an era of rapid technological advancement, digital twins have emerged as a transformative force across industries. These virtual replicas of physical entities, powered by advanced technologies like deep learning and natural language processing, are revolutionizing how we understand, monitor, and optimize complex systems. From manufacturing plants to entire cities, digital twins are creating unprecedented opportunities for innovation and efficiency.
They are transforming the way industries operate and evolving toward increasingly sophisticated applications.
The Evolution of Digital Twins
The concept of digital twins originated in the early 2000s, primarily within the manufacturing and aerospace sectors. NASA pioneered early applications, using digital twins for space vehicle monitoring and simulation. Initially focused on physical assets like jet engines and oil rigs, these virtual replicas served primarily to improve operational efficiency and enable predictive maintenance.
However, since then the technology has undergone a remarkable transformation. Early digital twins relied on basic sensor data and simple modeling techniques. Today’s versions incorporate artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics to process complex data streams in real-time. Modern digital twins have evolved from simple monitoring tools into sophisticated platforms capable of complex simulations, real-time optimization, and predictive analysis. They now integrate vast networks of IoT sensors, advanced machine learning algorithms, and real-time data processing capabilities to create increasingly accurate and valuable virtual representations. Industries across the spectrum have recognized the potential of digital twins, something that is evident from the growth trajectory of the technology in recent years.
Market Growth and Technological Milestones
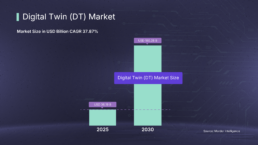
According to Grand View Research, the global digital twin market reached $16.75 billion in 2023, with projections showing a remarkable CAGR of 37.87% from 2025 to 2030. This growth reflects the technology’s maturity, its expanding applications across industries and its ability to help organizations achieve cost efficiencies.
Technology platforms are revolutionizing how industries create and utilize digital twins, enabling unprecedented levels of collaboration and simulation capabilities. These advanced platforms support real-time cooperation across global teams, physics-accurate simulations, and integration with multiple software tools, creating a new paradigm for virtual modeling and testing.
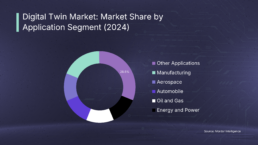
Industry adoption has been particularly strong in specific sectors. The oil and gas industry, for instance, has been at the forefront of digital twin implementation, with Hexagon reporting that 43% of companies in this sector had deployed digital twin technology by 2022. These implementations have yielded impressive results, including substantial reductions in maintenance costs, improved equipment uptime, and enhanced safety metrics.
Transforming Industries
Manufacturing and Industrial Applications
The manufacturing sector has emerged as a primary beneficiary of digital twin technology. Modern factories utilize digital twins to create virtual representations of entire production lines, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of manufacturing processes.
For example, Volkswagen’s implementation of digital twins in their paint shops has resulted in significant energy savings and quality improvements. The technology enables manufacturers to identify and resolve potential issues before they impact production, leading to substantial cost savings and efficiency gains.
Smart Cities and Urban Planning
The application of digital twins in urban environments represents one of the most ambitious implementations of this technology. Cities like Singapore and Dubai have developed comprehensive digital twin programs that transform urban planning and management. Virtual Singapore, a pioneering project in this space, demonstrates the potential for digital twins to address complex urban challenges.
These urban digital twins integrate data from multiple sources, including traffic systems, utility networks, and environmental sensors, to create detailed virtual representations of city infrastructure. This integration enables city planners to simulate various scenarios, from traffic pattern changes to emergency response situations, leading to more informed decision-making and improved urban services.
Healthcare Systems and Operations
Modern hospitals utilize digital twins to optimize everything from patient flow to equipment maintenance, creating more efficient and responsive healthcare environments.
Healthcare facilities have implemented digital twins to:
Model and optimize patient movement through facilities
Predict and prevent equipment failures
Improve resource allocation and staff scheduling
Enhance emergency preparedness and response
Monitor and control environmental conditions
The Cleveland Clinic’s implementation of digital twins for operating room management demonstrates the technology’s potential to improve healthcare efficiency and patient outcomes.
Infrastructure and Energy
Power plants, grid networks, and renewable energy installations utilize digital twins for real-time monitoring and optimization. These applications have proven particularly valuable in integrating renewable energy sources into existing power grids and managing the complexities of modern energy systems.
Emerging Applications and Future Horizons
The evolution of digital twin technology points toward a future where virtual and physical worlds become increasingly interconnected. Current trends and emerging technologies suggest several key directions for development that will shape how digital twins are implemented and utilized across industries.
Enhanced AI Integration
Artificial intelligence is becoming more sophisticated in its ability to analyze and act upon digital twin data. Advanced machine learning algorithms are enabling digital twins to move beyond simple simulation to predictive and prescriptive capabilities. For example, a major aerospace manufacturer is developing digital twins that can not only predict maintenance needs but also autonomously adjust aircraft component designs based on performance data across their fleet.
Improved Simulation Capabilities
Next-generation digital twins will offer unprecedented levels of simulation accuracy and complexity. Quantum computing developments are opening new possibilities for simulating molecular-level interactions in pharmaceutical development. In urban planning, improved simulation capabilities are enabling digital twins to model complex scenarios involving millions of variables, from climate change impacts to population movement patterns.
Greater Autonomy in Decision-Making
As digital twins become more sophisticated, their role in decision-making is expanding. Manufacturing facilities are experimenting with systems that can autonomously adjust production parameters based on real-time market demand and resource availability. However, this increased autonomy raises new questions about human oversight and control mechanisms. A European chemical plant recently implemented a hybrid system where their digital twin can make routine operational decisions while requiring human approval for significant changes.
Expanded Personal Applications
The concept of personal digital twins is evolving beyond simple health monitoring to encompass broader aspects of individual life and decision-making. Healthcare providers are developing digital twins that can simulate patient responses to different treatments, while educational institutions are exploring personalized learning systems that adapt to individual student progress. These applications point toward a future where personal digital twins could serve as digital advisors, helping individuals make more informed decisions about their health, education, and daily activities.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Digital twins are increasingly intersecting with other emerging technologies, creating new possibilities for interaction and application. The integration with blockchain technology is enabling more secure and transparent supply chain digital twins. Meanwhile, the development of 5G and eventually 6G networks will enable real-time synchronization of digital twins across vast distances with minimal latency. The rise of edge computing is also transforming how digital twins process and analyze data, enabling more responsive and efficient operations.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
The rapid advancement of digital twin technology brings forth a complex web of ethical considerations that industries must carefully navigate. These challenges transcend technical hurdles, touching on fundamental questions of privacy, accountability, and human agency in an increasingly digitized world.
Privacy and Data Protection
The implementation of digital twins requires vast amounts of data collection and processing, raising significant privacy concerns and calling for sophisticated measures to abate them.
Examples:
- An automotive plant in Germany recently faced pushback from labor unions when its digital twin system was found to be collecting more granular data about individual worker performance than had been disclosed, leading to concerns about surveillance and worker privacy.
- Singapore’s digital twin initiative collects data from millions of IoT sensors throughout the city, also creating detailed digital footprints of citizens’ daily movements and activities as a byproduct. The city has had to implement sophisticated anonymization protocols and strict access controls to protect citizen privacy while maintaining the system’s utility.
- A major hospital in the United States recently developed a system that creates anonymous patient flow models while maintaining individual privacy, demonstrating how careful design can address these concerns.
Bias and Fairness
Digital twins, like all AI-driven systems, can perpetuate and amplify existing biases if not carefully designed and monitored. In urban planning applications, for instance, digital twins might inadvertently prioritize services for certain neighborhoods based on historical data that reflects existing socioeconomic disparities.
Examples:
- A European city’s traffic optimization system recently came under scrutiny when it was discovered that its recommendations consistently favored routes through wealthier neighborhoods, potentially increasing traffic burden in less affluent areas.
- A manufacturing plant in Asia found that its digital twin’s workforce optimization algorithms were unintentionally discriminating against older workers by assigning them to less desirable shifts, based on historical performance data that reflected systemic biases.
Autonomy and Human Agency
As digital twins become more sophisticated in their decision-making capabilities, questions arise about the appropriate balance between automated and human decision-making. In healthcare settings, digital twins might recommend treatment plans or resource allocations, but the final decision must remain with human medical professionals.
Examples:
- A hospital in Canada implemented a system where their digital twin provides recommendations for patient scheduling and resource allocation, but requires human approval for any changes that could impact patient care.
- Dubai’s smart city initiative includes a human-in-the-loop system where key decisions suggested by the digital twin require validation from city officials before implementation.
Accountability and Liability
The question of who bears responsibility when digital twin systems make errors or cause harm is increasingly complex. In manufacturing, for instance, if a digital twin’s predictive maintenance system fails to identify a critical equipment failure that leads to an accident, determining liability becomes complicated. Is the software developer responsible? The company operating the system? The manufacturers of the sensors providing the data?
A recent case in the energy sector highlighted this challenge when a power plant’s digital twin failed to predict a critical component failure, leading to a temporary shutdown. The incident involved multiple stakeholders: the software provider, the sensor manufacturer, the system integrator, and the plant operators. The resulting legal discussion highlighted the need for clear frameworks defining responsibility and liability in digital twin implementations.
Technical and Social Challenges
The technical challenges of implementing digital twins are inextricably linked with social and ethical considerations.
When a major port facility implemented a digital twin system to optimize container handling, they found that workers were initially skeptical of the system’s recommendations, highlighting the need for transparent communication and gradual implementation strategies.
Cultural and Global Considerations
The implementation of digital twins must also consider cultural differences and global variations in privacy expectations and regulatory frameworks. What might be acceptable data collection in one culture could be considered invasive in another.
For example, a multinational manufacturing company found that its digital twin implementation needed significant modifications across different global locations to accommodate varying cultural norms and regulatory requirements.
Urban digital twins face similar challenges when implemented across different cultural contexts. A smart city system that works well in one country might need substantial modification to be acceptable in another, based on different cultural attitudes toward privacy and government oversight.
Regulatory Frameworks and Governance
Comprehensive regulatory frameworks are required to ensure a balance innovation with safety, security, and ethical considerations while providing standardization across industries and borders. Current regulatory developments are shaped by lessons learned from early implementations and emerging challenges across different sectors.
Data Protection Standards
The handling of sensitive data within digital twin systems requires robust protection standards. The European Union’s GDPR has become a benchmark for data protection, influencing how digital twin implementations handle personal and industrial data.
Interoperability Requirements
As digital twins become more interconnected, the need for standardized communication protocols has become critical. The Digital Twin Consortium, comprising major technology companies and industrial players, is working to establish common standards for digital twin implementations. For example, Singapore’s digital twin initiative required the development of standardized protocols to enable communication between different systems managing traffic, utilities, and emergency services.
Security Protocols
The integration of digital twins with critical infrastructure necessitates robust security measures. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed specific guidelines for securing digital twin implementations in critical infrastructure. These protocols became especially relevant after a series of cybersecurity incidents targeting industrial digital twins. including a 2023 attempt to compromise a power plant’s optimization systems.
Industry-Specific Regulations
Different sectors require tailored regulatory approaches to address their unique challenges. In healthcare, the FDA has begun developing guidelines for the use of digital twins in medical device testing and patient care planning. Similarly, the aviation industry has established specific requirements for digital twins used in aircraft design and maintenance, ensuring they meet stringent safety standards.
International Cooperation
International organizations are working to establish frameworks for cross-border data sharing and system integration. For example, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is developing global standards for digital twin implementations, while international working groups focus on addressing challenges in global supply chain digital twins.
Digital twins represent a transformative technology that continues to evolve and expand in scope and capability. From their origins in industrial applications to their emerging role in personal and urban environments, digital twins are reshaping how we interact with and optimize the world around us. As the technology matures, careful consideration of ethical implications and regulatory requirements will be crucial in ensuring its responsible development and deployment.