In 2024, India experienced 255 days of extreme weather events, which is 93% of the year! These events caused over 3,200 deaths, destroyed over 235,000 buildings, and damaged crops across 3.2 million hectares. In fact, no part of the world was spared from crippling climate disasters in 2024. Floods in China cost $15.6 billion and killed 315 people; Typhoon Yagi battered southwest Asia, killing more than 800 people.
The answer to climate change is clear: sustainability. Embracing sustainable solutions isn’t just the right thing to do; it is essential for the survival of our planet, our community, and future generations. By prioritizing environmental protection, fostering economic growth, and championing social equity, you can help create systems that enhance well-being and reduce the impacts of climate change. Together, we can tackle today’s challenges and secure a healthier, fairer, and more sustainable world for future generations. Ready to make a difference? Let’s get started.
What is sustainability?
People and nature need to coexist in a way that supports current and future generations. Sustainability seeks to create systems and practices that support long-term resilience, well-being, and harmony between people and the planet.
“Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
-UN World Commission on Environment and Development
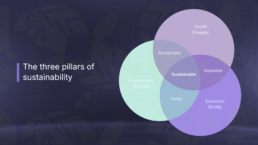
The three pillars of sustainability
Environmental sustainability: Saving the planet
Environmental sustainability is like tending a garden–every choice we make influences the ecosystem of the garden. It focuses on conserving natural resources and biodiversity to maintain ecological balance. By conserving natural resources, using renewable energy like solar and wind, and cutting back on waste through recycling and reusing, we nurture the balance needed for life to thrive.
But climate change, driven by greenhouse gas emissions, poses a significant threat to sustainability by altering weather patterns, increasing sea levels, and disrupting habitats. Deforestation adds to the problem, reducing the planet’s capacity to absorb carbon dioxide and protect biodiversity. To counter these threats, we must adopt innovative practices that conserve, reduce emissions, and safeguard our natural world.
Economic sustainability: Building a future that thrives
Economic sustainability isn’t just about making money—it’s about creating a system where resources are used efficiently, benefits are distributed fairly, and future generations inherit opportunities, not debt. For example, a business that thrives by adopting renewable energy saves on costs and reduces environmental impact, creating long-term resilience.
For individuals, economic sustainability means balancing today’s needs with tomorrow’s security. Imagine a family that embraces energy-efficient appliances or invests in local businesses—they’re saving money and strengthening their community’s economy. On a larger scale, governments that prioritize green infrastructure create jobs, reduce climate risks, and ensure steady economic growth. A key concept in economic sustainability is the circular economy, focusing on designing products and systems that reduce waste through reuse, recycling, and repurposing materials, thereby extending the lifecycle of resources.
Inaction has steep costs. Climate-related disasters disrupt supply chains, spike food prices, and lead to job losses. But by embracing economic sustainability, we not only shield ourselves from these risks but also build a future where growth, fairness, and environmental care coexist. Economic sustainability isn’t an option—it’s a necessity for prosperity.
Social sustainability: Building stronger communities
Social sustainability is about building inclusive communities where everyone has access to basic needs and gets the opportunity to thrive. It means ensuring quality education, healthcare, and employment are accessible to all, enabling individuals to reach their full potential.
Today’s global challenges make social sustainability more urgent than ever. Food insecurity and economic instability push families into poverty, while climate-induced migration disrupts lives. By supporting vulnerable groups and promoting inclusive growth, we can bridge gaps and ensure fair access to resources.
Global commitments to achieving sustainability
Achieving sustainability involves navigating a range of challenges including resource management, addressing climate change, technological limitations, raising investment and funding, and something as basic as encouraging cultural and behavioral change among people. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving collaboration among governments, businesses, communities, and individuals. Recognizing the urgency of sustainability, international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, have set clear targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and limiting global temperature rise.
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The UN SDGs provide a global framework for achieving sustainability by 2030. Comprising 17 goals, they address critical areas such as poverty, inequality, climate action, and environmental protection.
Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement is a landmark international treaty on climate change that aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help countries adapt to climate change.
The Paris Agreement’s main goals include:
- Limiting temperature rise: “Pursue efforts” to limit global temperature rises to 1.5°C, and to keep them “well below” 2°C above those recorded in pre-industrial times.
- Reducing emissions
- Adapting to climate change
- Providing financing to developing countries
Are we doing enough?
The short answer is NO! A stark disparity exists between the pledges made by governments, corporations, and international bodies and the actions taken to fulfill them. Many countries, especially high-income ones, have set ambitious net-zero targets but continue to rely heavily on fossil fuels for their energy needs. Similarly, some major corporations have made bold sustainability promises, yet their supply chains are still linked to unsustainable practices like deforestation and exploitation of natural resources. Then there is the phenomenon of “greenwashing,” which has further eroded trust in sustainability commitments.
Countries have pledged to reduce emissions, but many have not translated these promises into concrete policies or actions. The UN’s 2023 SDG Progress Report highlights that many countries are off track in meeting targets related to clean energy, responsible consumption, and reduced emissions. SDG 13 (Climate Action) has seen limited advancement.
In fact, global temperature in 2024 hit record 1.55°C over pre-industrial level. According to the UN Emissions Gap Report, the world is on track for a temperature rise of 2.4°C to 2.6°C by the end of the century. The emissions reduction targets set for 2030 are not being met by most major economies. Although climate change is recognized as a global issue, national policies often prioritize short-term economic gains over long-term environmental goals.
The cost factor
One of the most significant hurdles is the initial cost of transitioning to sustainable systems. Many businesses are reluctant to invest in renewable energy technologies or sustainable supply chains due to the perceived financial risks and initial costs involved. Another barrier is the lack of awareness or education about sustainable practices.
The cost factor affects businesses and entire nations as well. Developing countries, particularly those in sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and Latin America, are disproportionately affected by climate change yet lack the financial resources to implement changes.
Sustainable solutions
Sustainable solutions integrate environmental protection, economic viability, and social equity to ensure long-term well-being and resilience for all communities.
Innovations and emerging technologies
- Renewable energy sources can help meet growing energy demands without emitting harmful gases or materials into the environment. Solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy provide clean alternatives to fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on non-renewable resources. Additionally, conserving and using less energy can help reduce environmental impact and defer the need for new energy sources.
- Reducing carbon emissions is a critical part of the transition to a more sustainable economy. Carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies are being used as viable tools for mitigating emissions from industrial processes. Startups like Climeworks are capturing CO₂ directly from the air, while companies like CarbonCure are injecting CO₂ into concrete to reduce its carbon footprint..
- Water resource management ensures the sustainable use and conservation of water supplies, balancing ecological needs with human demands. Over 40% of the world’s population lives in water scarce areas, making water management a priority.
- Green buildings that are designed, constructed, and operated sustainably to consume less water, use energy optimally, and conserve natural resources are a great sustainable environmental solution. This is important considering construction accounts for roughly one-third of global waste.
Economic solutions
- Corporate Sustainability Reporting involves disclosing a company’s environmental, social, and governance performance to demonstrate accountability and commitment to sustainable practices.
- Several countries including India, Japan, China and countries in the European Union require leading businesses to disclose their sustainability information along with their annual reports
- ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance and is a framework used to assess an organization’s business practices and performance on various sustainability and ethical issues.
- Green finance refers to investments and financial activities that support environmentally sustainable projects, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and promote resource efficiency. Examples of green finance include: green bonds, a type of climate change bond that helps finance projects to reduce carbon emissions, green asset-backed securities, green mortgages to buyers who purchase environmentally sustainable properties, Carbon finance (ethical investing that places a financial value on carbon emissions).
-
Circular economy is a system where products and materials are circulated through maintenance, reuse, refurbishment, remanufacture, recycling, and composting. One of the best-known examples of the circular economy is recycling plastic. These three actions that can help achieve a circular economy:
- Reduce: Buy less and use fewer materials.
- Reuse: Use items multiple times.
- Recycle: Recycle products and packaging.
Social solutions
- Poverty alleviation addresses the root causes of socioeconomic instability and environmental degradation as poverty often leads to unsustainable practices, such as over-exploitation of natural resources.
- Diversity and inclusivity, when embraced, ensure that all individuals have equal opportunities and representation.
- Community engagement in decision-making processes ensures that local needs and voices are considered in development projects.
- Education for all, regardless of socioeconomic status, promotes equal opportunities and social mobility.
- Equitable healthcare provides accessible and affordable healthcare services, helps improve quality of life, and reduces health disparities.
- Fair labor practices, such as fair wages, safe working conditions, and workers’ rights protection, enhance job quality and social equity.
As individuals, businesses, and communities, we each have a role to play in making our planet sustainable. It’s time to turn over a new leaf: by planting seeds of sustainable practices in our daily lives, supporting green initiatives, and pushing for systemic changes that truly move the needle. By working together, we can build a more sustainable world and ensure a better future for generations to come.