The final frontier is no longer a passive opportunity—it’s a strategic imperative. What was once the domain of science fiction has transformed into a critical economic battlefield, where innovative nations and forward-thinking enterprises are redefining the boundaries of technological and economic potential. The space economy represents more than an emerging market; it’s a transformative force reshaping global competitiveness, technological innovation, and sustainable development.
Understanding the Space Economy
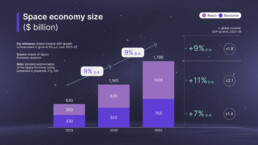
The global space economy, valued at $630 billion in 2023, encompasses far more than just rockets and satellites. It can be divided into two main segments:
Backbone Applications ($330 billion)
These are direct space-related revenues from:
- Satellite systems
- Launch vehicles
- Space hardware
- Direct services (TV broadcasting, GPS)
Reach Applications ($300 billion)
These are enabled by space technologies but generate revenue in terrestrial industries:
- Ride-sharing services (like Uber)
- Weather forecasting
- Parcel tracking
- Food delivery
- E-commerce
In the last few years, the space economy has become an integral part of driving the global economy. From job creation and economic growth to technological advancements with applications in other related industries— it offers a multitude of benefits. Today, it holds the power to even tackle some of the world’s biggest challenges like climate change and help build a more sustainable and inclusive future.
Growth Trajectory and Impact
The space economy is projected to reach $1.8 trillion by 2035, growing at an impressive 9% annually—nearly double the expected global GDP growth rate of 5%. For context, this growth puts it in league with:
- Semiconductor industry ($600 billion in 2021, 6-8% annual growth)
- About half the size of the global payments industry (projected $3.2 trillion by 2027
What is driving this growth? Here’s a quick look
Key Growth Metrics
- Satellite launches: 50%+ annual growth rate (2019-2023)
- Launch cost reduction: 90% decrease over 20 years
- Data costs: Projected 10% reduction by 2035
- Data demand: Expected 60% increase by 2035
- Private investment: $70+ billion peak in 2021-2022
- Earth observation: Achieved 15cm resolution capability
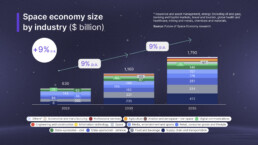
Seven industries will dominate the space economy, representing over 80% of combined backbone and reach revenues:
Supply Chain and Transportation
- Optimization of logistics networks
- Real-time tracking systems
Food and Beverage
- Last-mile delivery optimization
- Perishable goods monitoring
State-sponsored Defence
- Surveillance systems
- Secure communications networks
Retail, Consumer Goods/Electronics and Lifestyle
- E-commerce services
- Consumer electronics integration
Media, Entertainment and Sports
- Broadcasting services
- Sports tracking technology
State-sponsored Civil Programs
- Scientific research
- Environmental monitoring
- Disaster management
Digital Communications
- Global connectivity solutions
- Broadband services
Space economy size by industry ($ billion)
The space economy rests on three fundamental pillars that drive innovation, sustainability, and human advancement beyond Earth’s boundaries:
Core Pillars of the Space Economy
-
Satellite Technology
Modern satellites achieve sub-meter navigation precision while offering truly global communication coverage. Their impact extends from city planning to farming practices, with environmental monitoring systems projected to help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 2 gigatons annually by 2030.
-
Space Exploration and Research
This pillar represents humanity’s quest for knowledge through increasingly collaborative international missions. Using next-generation telescopes and probes, scientists are expanding our catalog of exoplanets while studying potentially habitable environments and cosmic phenomena.
-
Space Manufacturing and Resources
The unique zero-gravity environment enables revolutionary manufacturing techniques, including specialized 3D printing. This capability, combined with the potential to harvest valuable resources like water ice, Helium-3, and rare minerals, opens new possibilities for constructing large-scale space structures. The focus remains on sustainable practices through in-situ resource utilization – using materials found in space for space-based construction and operations.
Market Drivers: Propelling the Space Economy Forward
The remarkable growth of the space economy is powered by four interconnected forces that are fundamentally transforming how we access and utilize space:
Cost Reduction: Making Space Accessible
The economics of space have been revolutionized over the past two decades. Launch costs have plummeted by 90%, while satellite manufacturing benefits from unprecedented economies of scale. Data services continue to become more affordable, with the cost per bit declining steadily. These cost reductions have transformed space from an exclusive domain into an accessible business frontier.
Commercial Innovation: Accelerating Technological Progress
Innovation is reshaping space technology at every level. Components are becoming smaller yet more powerful through aggressive miniaturization. Advanced software is enabling autonomous operations and improved data processing. Meanwhile, manufacturing efficiency has leaped forward with automated production lines and standardized processes, allowing for faster, more reliable space hardware development.
Investment Diversification: Expanding Financial Horizons
The space sector is experiencing unprecedented financial interest. Private investment has reached record levels, attracted by new market applications ranging from satellite communications to space tourism. The investor base has broadened significantly, including venture capital, private equity, and even retail investors, creating a robust funding ecosystem for space ventures.
Cultural Momentum: Building Public Support
Space has captured public imagination like never before. Growing public engagement through media coverage and educational initiatives has created widespread support for space activities. Governments worldwide are increasing their space budgets and developing supportive policies. Commercial companies are actively participating in space activities, from satellite deployment to space tourism, further normalizing space as a domain for business and innovation.
A look at the countries that are leading the space race
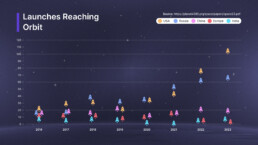
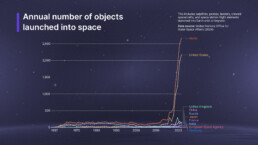
In 2023, global space activities reached unprecedented levels, with 223 orbital launch attempts and 2,911 satellites deployed. The United States led with 109 launches, followed by China with 67, and Russia with 19. Commercial satellites dominated, accounting for 2,626 of the total, reflecting the private sector’s growing influence. Military space operations saw advancements in surveillance, imaging, and signals intelligence, with notable contributions from the U.S., China, and Russia. Both the International Space Station and China’s space station expanded their operations, hosting multiple crewed missions. However, the surge in launches intensified concerns over space debris, underscoring the need for enhanced orbital traffic management.
The promise of space: What can space help us tackle?
Looking Forward: The Space Economy’s Promise
The space economy is not merely an industry—it’s a strategic platform for global problem-solving and economic reinvention. As we approach 2035, with a projected market value of $1.8 trillion, this sector transcends traditional economic boundaries. It represents a new strategic domain where technological innovation, economic opportunity, and global challenges converge.
For forward-thinking organizations and nations, the space economy is a critical battleground of innovation. The decreasing cost of space access, combined with unprecedented technological capabilities, means that strategic positioning is no longer optional—it’s essential. Those who view space not as a distant frontier, but as an integral part of their strategic ecosystem, will lead the next wave of global economic transformation.
This isn’t just about reaching for the stars—it’s about reimagining what’s possible for our planet, our economies, and our collective future. The space economy is the ultimate strategic canvas, where imagination, technology, and ambition intersect to solve humanity’s most pressing challenges.