Have you heard of “Appeal to AI”? It is a tactic used by individuals to invoke AI-generated responses to bolster their arguments and lend authority to their claims. This raises a complex question, especially as GenAI models like ChatGPT et al generate content based on patterns in data rather than verified truths. An LLM (Large Language Model) only picks up information from the web and presents it to us in an understandable format. By its nature, it cannot determine whether what it’s saying is true or false. This highlights the paradox of GenAI: while designed to enhance information accessibility, it can inadvertently undermine credibility when over-relied upon without critical evaluation. Another way to look at it is that when the productivity boost provided by GenAI (or Generative AI) becomes widespread, it creates saturation and trust erosion, making GenAI a double-edged sword. This paradox challenges us to navigate the fine line between embracing technological advancements and safeguarding the authenticity of our information ecosystem.
The Promise of GenAI
With tools that can generate text, images, music, and videos with remarkable proficiency, GenAI has transformed content creation, providing several potential benefits:
Enhanced Creativity and Innovation
AI’s ability to analyse vast datasets to identify patterns and generate novel ideas, serves as a catalyst for human creativity. For instance, AI-generated art is allowing artists to explore uncharted territories. The collaboration between AI and human creators can lead to innovative outcomes that were previously unimaginable.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
AI can automate routine tasks across many industries, enabling professionals to focus on more strategic and creative endeavors. For example, in journalism and marketing, AI-driven tools can draft articles, create marketing copy, and even design graphics, significantly reducing the time and resources required for content production.
Personalised User Experiences
GenAI helps deliver personalised user experiences by leveraging its ability to analyse vast datasets, generate context-aware content, and adapt outputs to individual user preferences. This personalisation enhances user engagement and satisfaction, as consumers receive content that resonates with their interests and needs.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
AI-generated content can bridge language barriers and make information more accessible. For instance, AI models can automatically generate captions, Alt Text for images and audio descriptions for videos, making them more accessible for people who are deaf or hard of hearing, or visually impaired.
The Erosion of Trust
Ironically enough, it is because of this potential that GenAI poses significant challenges, particularly concerning trust and authenticity:
Proliferation of Disinformation
The ease with which AI can generate realistic yet false information has led to an increase in disinformation. It allows malicious actors to craft persuasive false narratives at an unprecedented scale and speed Deepfakes – synthetic media where a person’s likeness is manipulated – show how false narratives can manipulate public opinion, incite violence, and even hoodwink people into a false sense of security, thereby getting them to unknowingly engage in fraud.
Recent Examples:
- Political Manipulation: In 2024, the U.S. Department of Justice exposed sophisticated tactics by Russian state-backed entities using GenAI to influence American politics. These methods included AI-generated ads and counterfeit news sites aimed at manipulating public opinion during the presidential race.
- Unauthorised Use: Actor Anil Kapoor secured a legal victory in the New Delhi High Court against unauthorized AI use of a large number of distorted videos, gifs, and emojis bearing his likeness. The court prohibited the misuse of his persona, setting a precedent for protecting celebrities’ rights against AI-generated content.
- Deepfake Scams: In Feb 2024, a Hong Kong employee of a multinational company was deceived by a deepfake video call featuring realistic imitations of the CFO and colleagues, leading to a $25.6 million transfer. The scam began with an email requesting a confidential transaction and was uncovered a week later. This incident highlights the alarming sophistication of deepfake technology in financial fraud.
Undermining of Authenticity
As AI-generated content becomes more prevalent, distinguishing between genuine and fabricated information becomes increasingly challenging. This blurring of lines can lead to skepticism, where individuals question the authenticity of all content, even that which is legitimate. The concept of the ‘liar’s dividend’ illustrates this phenomenon, where the mere possibility of content being AI-generated allows real events to be dismissed as fake.
Recent findings illustrate this phenomenon:
- Deepfake Exploitation: A fabricated video of President Zelensky surrendering to Russia spread doubt, impacting Ukrainian morale and global perspectives on the war.
- Fake War Images: AI-generated visuals from the Israel-Hamas conflict misrepresented events, misleading audiences and fueling emotional reactions.
Impact on Human Creativity
Over-reliance on AI tools can adversely affect human creativity by diminishing authenticity and fostering dependency. According to a blog post by Andres Fortino at NYU’s School of Professional Studies, excessive dependence on AI may overshadow the unique nuances of human thought, leading to a loss of genuine creativity. For instance, AI-generated music, such as Sony’s “Daddy’s Car,” raises questions about the boundary between authentic human creativity and machine mimicry.
Ethical and Legal Challenges
The rise of AI-generated content brings forth ethical dilemmas and legal complexities. Issues such as intellectual property rights, accountability for AI-generated misinformation, and the potential for AI to perpetuate biases are pressing concerns that require comprehensive frameworks to address these challenges.
Navigating the Paradox
To harness the benefits of GenAI while mitigating its risks, a multifaceted approach is essential:
Transparency and Disclosure
Transparency and disclosure mechanisms are essential tools for building and maintaining trust in AI-generated content, though their effectiveness varies significantly based on implementation method and context.
The most effective approaches combine multiple disclosure methods:
Machine-readable watermarking embedded during content creation and distribution, which provides tamper-resistant identification and authentication. A notable example is Meta’s AudioSeal system, specifically designed for detecting AI-generated speech.
Visual labeling systems that platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok have implemented, requiring clear indicators for synthetic media using terms like “synthetic,” “fake,” or “altered”.
However, transparency alone isn’t sufficient. In a study across the US, China, Mexico, Brazil, and India, terms like “deepfake” and “manipulated” were often associated with misleading content regardless of AI involvement. Additionally, 96% of online deepfakes in 2019 were found to be pornographic, highlighting how disclosure requirements must be paired with robust detection and enforcement mechanisms to effectively protect users and maintain trust.
Regulation and Ethical Guidelines
A comprehensive regulatory framework for AI content creation must effectively prevent misuse and build trust. Key components include:
Mandatory (not voluntary) content disclosure requirements, as malicious actors frequently evade labeling or deliberately mislabel AI-generated content.
Implementation responsibilities placed at both content creation sources and distribution platforms – critical given incidents like AI-generated explicit images reaching 47 million views on social media.
“Regulatory sandboxes” for testing governance approaches, involving citizens in evaluating disclosure requirements and understanding societal impacts.
These technical measures must be supported by comprehensive user education, as research shows many struggle to identify AI content even when labeled.
Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education are crucial elements in helping users navigate and critically assess AI-generated content in today’s digital landscape. Despite technological solutions like watermarks and labels, many individuals struggle to identify and understand the implications of AI-generated content even when properly marked.
Research demonstrates the urgent need for comprehensive education: a single face photo can now be used to generate explicit content, as evidenced by a 2023 incident in Spain where over 20 young girls received AI-generated explicit images of themselves. Similarly, social media’s content distribution algorithms tend to amplify emotional and agitating content, potentially increasing the spread of synthetic material.
Educational initiatives must focus on:
- Understanding how AI content affects trust in media
- Recognizing the spectrum of synthetic content from minimally edited to fully AI-generated
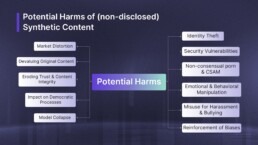
- Building awareness of potential misuse, from identity theft to manipulation of democratic processes
- Developing critical assessment skills for digital content authenticity
This educational foundation complements technological safeguards and regulatory frameworks, creating a more resilient and informed digital society.
Technological Solutions
GenAI offers unparalleled efficiency and can help augment human creativity. But it’s still evolving, and as such we need to use it more consciously and ethically to counter the significant risks it poses to trust and authenticity. By proactively addressing these challenges through transparency, regulation, education, and technological innovation, we can navigate this paradox.
Investment in AI detection technologies is critical, with several cutting-edge approaches already showing promise in identifying synthetic content. The Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity, supported by industry leaders including Adobe, Microsoft, and Google, has developed the C2PA standard that combines cryptographic watermarking with metadata embedding for content verification.
Key technological developments include:
- Meta’s AudioSeal – the first audio watermarking technique specifically designed for localized detection of AI-generated speech
- Google’s SynthID – a system that embeds invisible digital signatures in AI-generated photos and music, allowing for verification through specialized detectors
- Statistical watermarking tools being developed by researchers for OpenAI that analyze token selection patterns.
However, current detection tools face significant challenges. OpenAI’s own detection tool, launched in January 2023, was discontinued by June due to low accuracy rates – correctly identifying only 26% of AI-written text while incorrectly flagging 9% of human-written content. Additionally, detection tools have shown bias against non-native English speakers, whose submissions are more likely to be incorrectly flagged as AI-generated.